News Center
Automotive Air Suspension:Definition,Structure,Principle
Published on.
2024-04-28 10:12
Source
The suspension is an important part of automobile chassis, which is responsible for connecting wheels and body, transmitting various forces and moments, and buffering and absorbing the impact caused by uneven road surfaces, thereby ensuring the smooth operation of the vehicle and ride comfort.
The suspension system is the general term for all force transmitting connection devices between the body and the wheels. It not only supports the weight of the vehicle, but is also responsible for maintaining the wheel alignment parameters.
1.The main components of the suspension system
Elastic Elements: such as coil springs, leaf springs or air springs, which support the weight of the vehicle and absorb shocks.
Shock Absorbers: Also known as dampers, they are used to suppress the vibrations of the springs and improve driving stability.
Steering Linkage: Such as control arms, tie rods, steering knuckles, etc., which are used for wheel positioning to ensure the correct direction of the wheels when the vehicle turns.
Stabilizer Bars: Also known as anti-roll bars, they are used to reduce the body roll of the vehicle during turns.
Other Auxiliary Components: Such as bushings, ball joints, suspension arms, etc., which serve to connect, support, and reduce friction.

2.Suspension Features:
Load-bearing Capacity: The suspension must bear the weight of the vehicle and the impact load on uneven surfaces.
Shock Absorption: It absorbs the impact from uneven road surfaces through elastic elements, reducing discomfort for passengers.
Wheel Alignment: The steering linkage maintains the correct positioning of the wheels, which is crucial for the vehicle's handling and stability.
Adaptability: It can adapt to different road conditions and driving habits, providing stable driving performance.
Handling: The design of the suspension affects the vehicle's handling response, including roll control during turns and pitch control during acceleration and braking.
Durability: The suspension system needs to withstand long-term cyclic loads, so it requires good durability and reliability.
Structural Complexity: The design of the suspension system needs to consider a variety of factors, such as comfort, handling, cost, and spatial layout.
3.Forms of Suspension:
A. Based on structure, it can be divided into independent suspension and non-independent suspension.
Independent suspension means there is no rigid axle connecting the left and right wheels, and the movement of one wheel does not affect the other. The structure of independent suspension is relatively complex and more expensive. Common types of independent suspension include MacPherson suspension, double wishbone suspension, and multi-link suspension.
(1) MacPherson Suspension: The control arm is an A-shaped arm that can bear the lateral and longitudinal forces on the lower part of the wheel. It has the advantages of compact structure and high integration, but due to the constraints of the mechanism, it has poor lateral rigidity and insufficient suppression of vehicle pitch and torque steering.
(2) Double Wishbone Suspension: It has the same lower structure as the MacPherson suspension, which is an A-arm, and there is also an A-arm on the upper part of the wheel connected to the vehicle body.
(3) Multi-link Suspension: It has more control arms than a regular suspension, and suspensions with four or more control arms are generally called multi-link suspensions. The advantage is high design freedom, and the disadvantage is a large demand for layout space and high cost.
Non-independent suspension: It refers to a hard connection between the two wheels, and when one wheel moves, the other wheel is also affected. The common non-independent suspension is the torsion beam suspension.
Torsion Beam Suspension: The left and right wheels are connected by a torsion beam. The structure is relatively simple, and the cost is moderate. Although it is a non-independent suspension, its dynamic performance is close to that of an independent suspension and is suitable for the rear suspension of compact cars and SUVs.
B. Based on the control form, it can be divided into passive suspension, semi-active suspension, and active suspension.
(1) Passive Suspension: The stiffness and damping were set at the factory and are not adjustable. The advantage is a simple structure and low cost. The disadvantage is poor handling and comfort. The vast majority of vehicle currently use passive suspension. Applied to traditional passenger cars, representative model: Corolla.
(2) Semi-active Suspension: One of the stiffness and damping is adjustable, usually the damping is adjustable. The advantage is excellent performance and high reliability. The disadvantage is a small range of damping adjustment, and the stiffness cannot be continuously adjusted. Applied to mid-to-high-end passenger cars, representative models: Buick LaCrosse, BYD Tang.
(3) Active Suspension: Both stiffness and damping are adjustable. The advantage is higher vehicle stability, comfort, and passability, and adjustable vehicle height. The disadvantage is high cost, relatively complex structure, and high replacement frequency. Applied to luxury passenger cars, representative models: Mercedes-Benz S-Class, BMW 7 Series.
4.Air Suspension Definition
Air suspension is an automotive suspension system that uses air springs instead of traditional metal springs to support the vehicle. The core advantage of this system is the ability to provide adjustable ride height and improved ride comfort. Compared with traditional suspensions, the biggest difference is the upgrade of the elastic element and the addition of electronic control systems and air pumps.
5.Air Suspension Main Components:
Air Spring: As an elastic element, it replaces the traditional metal spring and can adjust the stiffness and vehicle height.
Air Compressor: Used to generate compressed air and deliver it to the air springs.
Air Tank: Stores compressed air for use by the air springs.
Control Unit (ECU): Controls the air compressor and exhaust valves based on signals from sensors, adjusting vehicle height and suspension stiffness.
Sensors: Including height sensors, speed sensors, etc., used to monitor parameters such as vehicle height, vehicle speed, and acceleration.
Electromagnetic Shock Absorber: Adjusts damping force according to the instructions of the ECU to adapt to different driving conditions.
6.Air Suspension Features:
Height Adjustment Capability: Air suspension can automatically or manually adjust the suspension height according to different driving needs and driving conditions, improving vehicle passability and adaptability.
Improved Comfort: Air springs have a larger compression stroke and lower stiffness, which can more effectively absorb the unevenness of the road, providing a smoother riding experience.
Automatic Stiffness Adjustment: By changing the pressure inside the air spring, air suspension can automatically adjust the stiffness to adapt to different loads and driving modes.
Improved Handling: Air suspension can adjust the suspension settings in real-time based on sensor inputs such as vehicle speed and steering, improving the vehicle's handling performance.
Adaptability to Complex Road Conditions: Air suspension can automatically adjust according to road conditions, improving the vehicle's driving stability on complex road conditions.
Higher Cost: Due to its complex structure and high technical requirements, the cost of air suspension is usually higher than that of traditional metal spring suspension systems.
7.Working Principle of Air Suspension
Sensors collect signals about the vehicle's body state and transmit them to the control unit ECU. The ECU outputs control information based on a series of algorithms, controlling the air supply system to operate. The air compressor in the air supply system intakes air, removes impurities and moisture through a dryer, and then sends it to the air tank. It is then delivered to the air springs at each wheel side through a distribution valve, thereby adjusting the suspension stiffness and damping.
8.Passenger Vehicle Air Suspension Advantages:
(1) Better Comfort: It can automatically adjust the suspension hardness according to road conditions and vehicle speed, thereby reducing the vehicle's bumps and vibrations and improving the stability and comfort of the vehicle.
(2) Higher Safety: It can automatically adjust the vehicle body height and hardness according to vehicle speed and steering angle, thereby improving the vehicle's stability and handling, reducing the risk of rollover and overturning. During high-speed driving and sharp turns, air suspension can more effectively control the vehicle's posture and improve driving safety.
(3) In line with the trend of automotive intelligence: Under the EE architecture, the automotive chassis also develops from the independent operation of each module to the integrated development of the XYZ chassis domain control. The air suspension with an electronic control system is easier to combine with intelligent vehicles, achieving precise control and integrating the XYZ chassis domain control.
9.Commercial Vehicle Air Suspension Advantages:
(1) Better Comfort, Stronger Damping Effect: Using compressed air to achieve a soft connection, it alleviates most of the impact from the road surface.
(2) Effectively Reduce Fuel Consumption, Improve Economic Benefits: When a vehicle with air suspension is in an unladen state, the axle can be lifted to reduce friction and thus lower fuel consumption. In addition, relying on the good shock absorption of the airbag, it can effectively reduce gear shifting frequency and acceleration and deceleration on bumpy roads, thereby reducing fuel consumption.
(3) Facilitate Quick Coupling and Uncoupling, Improve Transportation Efficiency: When a tractor with air suspension is engaged in quick coupling and uncoupling transportation, it can quickly achieve uncoupling and coupling by adjusting the airbag height, improving transportation efficiency.
(4) Facilitate Loading and Unloading at Different Height Docks: There are height differences between different cargo dock platforms. When a vehicle with air suspension docks for loading and unloading, it can adjust the airbag height according to the different heights of the dock platform, thereby adjusting the vehicle body height to facilitate the rapid loading and unloading of goods.
(5) Extend Tire Life, Protect the Road Surface: It can effectively reduce the impact between the tire and the road surface, reduce tire wear, and also reduce the load impact on the road, increasing effective protection of the road surface and reducing road maintenance and repair costs.

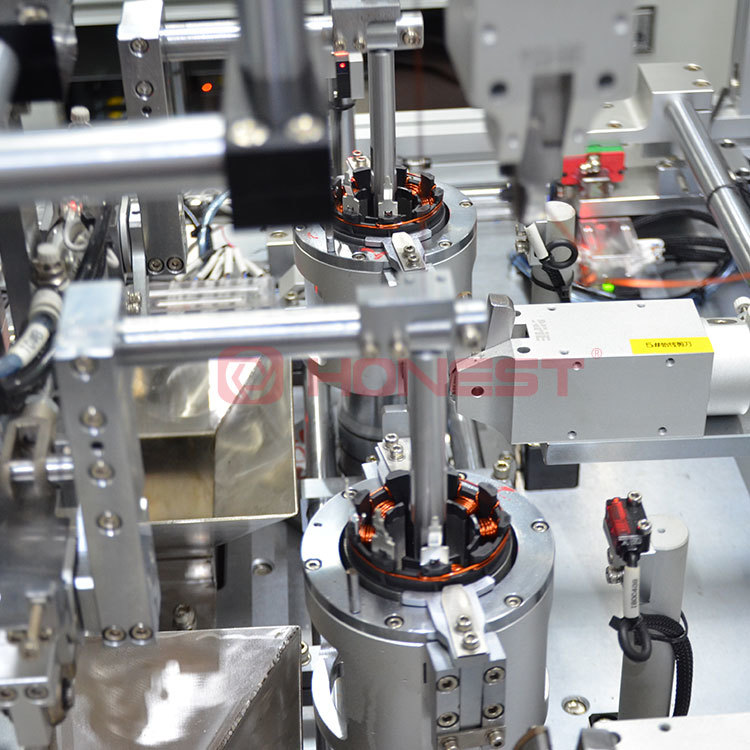
The picture shows HONEST HLS’s SG Damping Regulator Stepper Motor Assembly Line. It is used to produce non front/rear damping regulating valves. It is highly efficient, capable of product in approximately one second, boast a yield rate of up to 99% and its utilization rate up to 85%. It can save money and time during manufacturing process.
If you want to get more information, please contact us at any time.
Previous page
Next page
Related News