News Center
Fan Motor Production Line Structure
Published on.
2024-12-11 10:36
Source
In the automotive industry, the fan motor is the core component of the cooling system. Its working principle is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. The motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to drive the fan to rotate, thereby cooling the car engine. When we disassemble a fan motor production line in-depth, we can clearly see its precise internal structure, and behind all this is a complex assembly production process. This article will explore the key components, assembly production process and importance of fan motors from the perspective of disassembly.
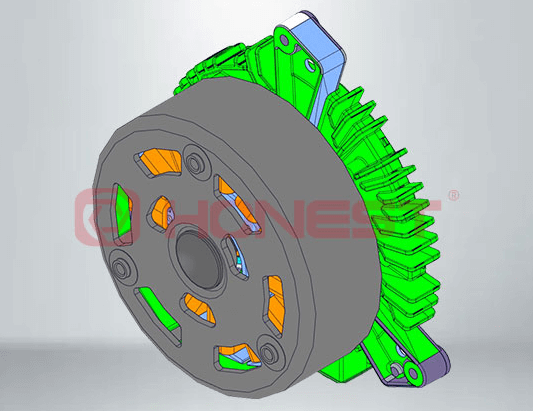
Key components of automotive fan motors and their functions:
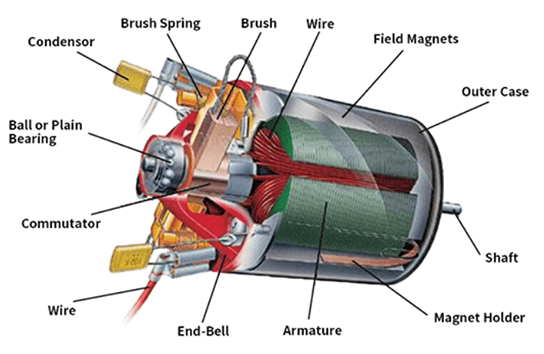
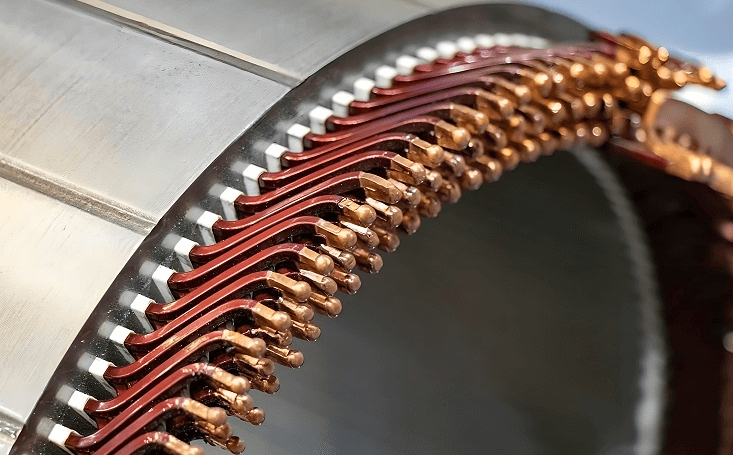
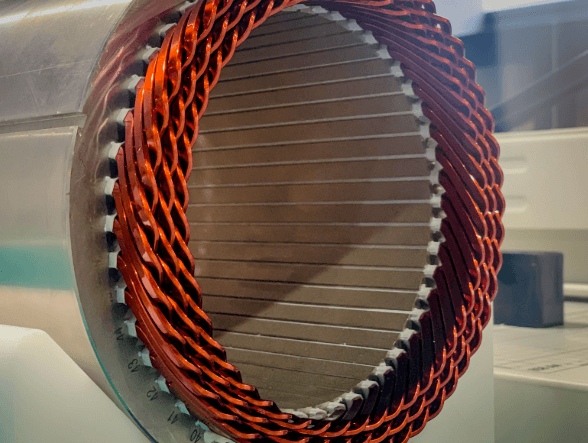
Stator: As the fixed part of the fan motor, it is mainly composed of an iron core and windings. When current passes through the windings, a rotating magnetic field is generated, which is used as a power source to drive the rotor.
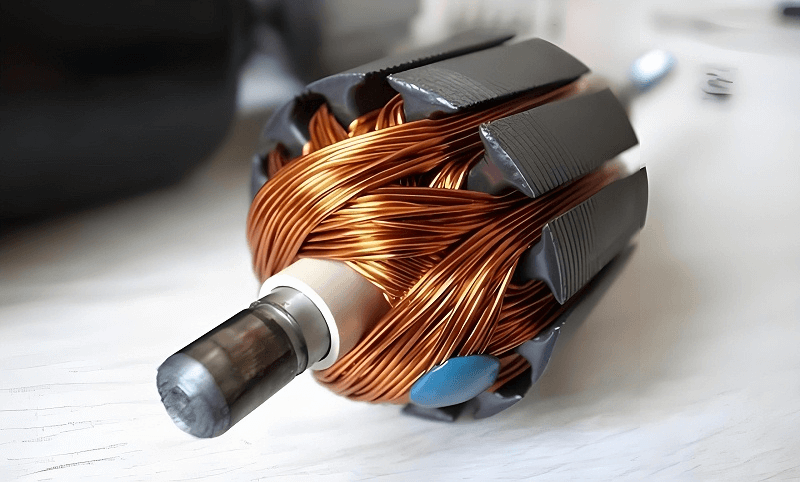
Rotor: Starts to rotate due to the rotating magnetic field generated by the stator, thus driving the fan blades. Usually consists of an iron core, windings and a shaft. Its balance and accuracy are critical to the smooth operation of the motor.
Other Components
Bearings: Support the rotor and allow it to rotate smoothly, reducing friction and wear.
Fan blades: fixed on the rotor shaft, generate wind flow through the rotation of the rotor to achieve cooling effect.
Cooling system: includes heat sink and fan, used to dissipate the heat generated when the generator is running to prevent overheating.
The production line processes of automobile fan motors include the stator section, rotor section, motor assembly section and fan section. The assembly processes of several key processes are extracted and introduced.
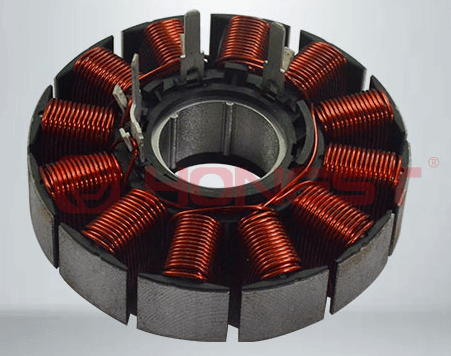
1. Winding machine: The module is automatically loaded to the winding station, and a double-station flying fork winding machine is configured. It automatically scans the code through product arrival sensing and uses automatic precision cable arrangement and servo tensioner to control the winding tension to ensure the uniformity and stability of the winding and improve the operating efficiency of the motor.
2. Clamp welding machine: The stator is automatically transported and loaded, and a double station is configured for clamp welding. The connecting piece is automatically clamped and welded, and the current, voltage, resistance, power and clamp welding pressure displacement curve are monitored in real-time to ensure that welding problems can be discovered in time during the clamp welding process and improve the welding quality. At the same time, a smoke purifier and a camera are configured to detect the effect after welding to ensure the cleanliness of the production environment and visual monitoring of welding quality.
3. Magnet assembly & heating and cooling machine: The magnetic tiles are automatically separated and discharged, and the camera takes pictures from the top to detect obvious defects in the appearance, and defective products are automatically discharged; then the casing is loaded onto the positioning fixture and assembled into the magnetic tile mold. The external support makes the magnetic tiles close to the casing and then sent to the high-frequency heating station to ensure the firm combination of the magnetic tiles and the casing, thereby improving the reliability and durability of the motor.
4. Weight removal balancing machine: The rotor is automatically scanned and loaded to the material exchange station for dynamic balancing test. The unbalanced amount is automatically cut during the test to improve the balance performance of the motor.
If the fan motor isn't assembled accurately, the overall performance of the fan motor will be affected as follows:
Reduced efficiency: Imprecise assembly may result in reduced motor efficiency and increased energy consumption.
Increased noise: Unbalanced rotors and bearings can cause increased noise during operation, affecting the driving experience.
Shortened lifespan: Improper assembly may cause the motor to overheat, accelerate component wear, and shorten the motor lifespan.
Safety risks: Motor failure may cause safety issues, such as fire risk due to overheating.
The disassembly and assembly process of automotive fan motors is a complex and delicate process involving multiple key components and processes. By strengthening quality control, optimizing production processes, and introducing intelligent equipment, the performance and reliability of automotive fan motors can be further improved, making greater contributions to the development of the automotive industry.
Previous page
Related News
2025-01-21