News Center
Hub Motor or Wheel-edge Motor, Who Will Dominate the Future?
Published on.
2023-04-25 13:23
Source
1. Introduction to Hub Motor Technology
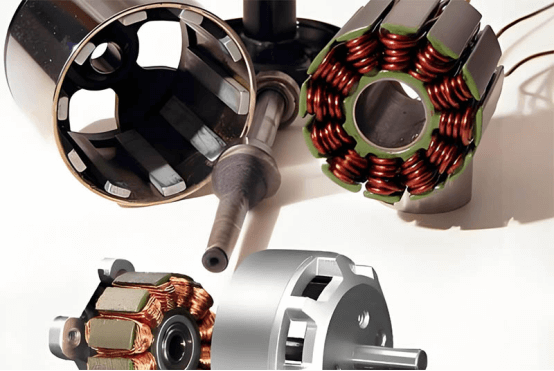
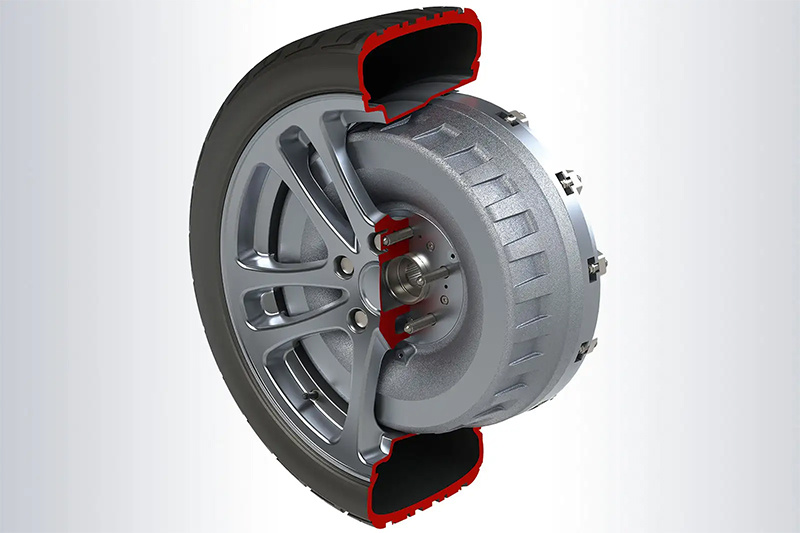
Hub motor technology, also known as in-wheel motor technology, is characterized by the integration of power, transmission and braking devices into the wheel hub, thus greatly simplifying the mechanical parts of electric vehicles.
Hub motor technology is not a new thing. As early as 1900, electric vehicles with front wheels equipped with hub motors were manufactured. In the 1970s, this technology was applied in fields such as mine transport vehicles.

Japanese manufacturers have developed in-wheel motors earlier and are currently in a leading position. International auto giants including GM and Toyota have also been involved in this technology.
The hub motor drive system is mainly divided into two structural types according to the rotor type of the motor: inner rotor type and outer rotor type.
Among them, the outer rotor type adopts a low-speed outer rotor motor, the maximum speed of the motor is 1000-1500r/min, there is no deceleration device, and the speed of the wheel is the same as that of the motor.
The inner rotor type uses a high-speed inner rotor motor and is equipped with a reducer with a fixed transmission ratio. In order to obtain a higher power density, the motor speed can be as high as 10000r/min.
With the advent of more compact planetary gear reducers, inner rotor hub motors are more competitive than low-speed outer rotor hub motors in terms of power density.
2. Advantages of Hub Motors
2.1 Many transmission parts are omitted, and the vehicle structure is simpler.
For traditional vehicles, clutches, transmissions, drive shafts, differentials and even transfer cases are all essential, and these components are heavy, making the structure of the vehicle more complex, and there are also problems that require regular maintenance and breakdowns rate problems.
Hub motors can solve this problem. In addition to a simpler structure, vehicles driven by hub motors can achieve better space utilization and higher transmission efficiency.
2.2 A variety of complex driving methods can be realized.
Since the hub motor has the characteristics of independent drive of a single wheel, it can be realized relatively easily whether it is front-wheel drive, rear-drive or four-wheel drive. Full-time four-wheel drive is very easy to implement on a vehicle driven by a hub motor.
At the same time, the in-wheel motor can achieve differential steering similar to that of a crawler vehicle through different rotation speeds or even reverse rotation of the left and right wheels, which greatly reduces the turning radius of the vehicle, and can almost achieve in-situ steering under special circumstances (but at this time the vehicle steering mechanism and The wear of the tires are greater), and it is valuable for special vehicles.
2.3 Facilitate the adoption of various new energy vehicle technologies.
Many new energy models use electric drive, so hub motor drive also comes in handy. Whether it is a pure electric vehicle, a fuel cell electric vehicle, or an extended-range electric vehicle, the hub motor can be used as the main driving force; even for a hybrid vehicle, the hub motor can also be used as a booster for starting or rapid acceleration.
At the same time, many technologies of new energy vehicles, such as braking energy recovery, can also be easily realized on in-wheel motor-driven models.
3. Disadvantages of Hub Motors
3.1 Increase the moment of inertia of the unsprung mass and the hub, which will affect the handling of the vehicle.
For ordinary civilian vehicles, some relatively lightweight materials such as aluminum alloy are often used to make suspension components to reduce the unsprung mass and improve the response speed of the suspension.

However, the hub motor just increases the unsprung mass considerably, and also increases the moment of inertia of the hub, which is detrimental to the handling performance of the vehicle. However, considering that most electric models are limited to transportation rather than power performance, this is not the biggest flaw.
3.2 The performance of electric braking is limited, and it takes a lot of power to maintain the operation of the braking system.
Many traditional power commercial vehicles are now equipped with auxiliary deceleration equipment that uses the principle of eddy current braking (that is, resistance braking), such as the electric retarder used in many trucks.
Due to the relationship between energy sources, electric braking is also the first choice for electric vehicles. However, for vehicles driven by hub motor, due to the small electric braking capacity of the hub motor system, it cannot meet the requirements of vehicle braking performance, and additional mechanical brake moving system are required.
However, for ordinary electric vehicles, without the vacuum pump driven by the traditional internal combustion engine, an electric vacuum pump is needed to provide brake boost, which means greater energy consumption. Even regenerative braking can recover some energy. If you want to ensure The efficiency of the braking system and the energy consumed by the braking system are also one of important factors affecting the cruising range of electric vehicles.
In addition, the working environment of the hub motor is harsh, and it is affected by water, dust and other aspects. It also has high requirements in terms of sealing. At the same time, the heat dissipation problem of the hub motor needs to be considered separately in the design.
4. Application Status of Hub Motor Technology
In recent years, the application of hub motor drive technology is mainly reflected in two aspects:
An integrated electric system developed by a research and development team represented by a tire manufacturer or an auto parts manufacturer;
Electric vehicles are jointly developed by vehicle manufacturers and hub motor drive system manufacturers.
Introduction to Wheel Side Motor
1. Wheel side electric drive axle definition
The wheel motor is installed on the side of the wheel to drive the wheel alone. The hub motor is the motor embedded in the wheel, the stator is fixed on the tire, and the rotor is fixed on the axle instead of transmitting power to the wheel through the transmission shaft.
Wheel side motor usually means that each driving wheel is driven by a separate electric motor, but the motor is not integrated in the wheel, but connected to the wheel through the transmission motor output shaft.
The wheel side motor is a motor installed on the side of the wheel to drive the wheel alone. On both sides are a motor and a reducer. The main reducer and differential are canceled. The comprehensive power consumption is relatively good. The wheel side motor drive system is convenient to realize the electronic Differential speed and torque coordinated control, braking energy can be recovered, and it has the unique advantage of high energy utilization rate.
2. Features and Technical Obstacles of Wheel Motors
Distributed drive technology is a relatively hot technology in recent years, and some companies have been researching distributed drives. Compared with the central drive system, the wheel drive system has a more concentrated and refined driving force, so it has received higher attention in the bus industry.
Although wheel drive has outstanding advantages, its technical problems cannot be ignored. At present, the main problems of the wheel drive system are concentrated on the control of the motor, which motor needs to work, and under what working conditions, it takes a long time to study.
When the vehicle is turning, the rotation speeds of the wheels on both sides are inconsistent. After the distributed drive cancels the differential, an electronic differential controller is needed to complete the turning. However, this domestic technology has not yet met the requirements for use.
The driving precision of the wheel drive system is very high, and it can even be accurate to the amount of torque and torque, but the finer the control, the more complicated it will be.
During the driving process of the vehicle, the calculation amount of its core component VMS (vehicle controller) is very large. Every time a motor or a node is added, the data processing amount of the VMS will increase exponentially.

At present, there is still no ideal solution to perfectly solve the differential speed problem of the wheel drive, especially the differential speed control on high-speed cornering and road bumps. In addition, due to the high unsprung quality of wheel-side motors, which affects comfort, only some bus companies currently use wheel-side drive technology.
3. Analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of wheel motors and hub motors
Both the wheel motor and the hub motor belong to the distributed electric drive axle, and both are driven by dual motors. The difference is that one puts the motor in the hub, and the other puts the motor beside the wheel.
At present, hub motors have two technical schemes of the inner rotor and outer rotor. First, popularize the difference between the inner rotor and outer rotor:
The rotor and the motor shaft rotate together, and the motor frame is fixed as an inner rotor motor.
The rotor rotates with the motor casing and the motor shaft is fixed, which is an external rotor motor.
Simply put, the former uses the shell as the stator, and the interior and the main shaft as the rotor, which is a traditional
The latter uses the outer casing as the rotor, and the inner and main shaft as the stator.
The inner rotor generally has few poles, high speed and small torque.
The outer rotor generally has more poles, lower speed and higher torque.
Conclusion
Judging from the current application, the wheel motor has begun to enter industrialization, while the hub motor is still in the batch application stage.
In terms of hub motors, the inner rotor and reducer scheme theoretically has a higher power density and a more compact structure, but due to the complexity of the technology, no mass-produced products have been seen yet. Although the outer rotor hub motor is large in size and heavy in weight, due to its relatively simple structure, few transmission chains, and high efficiency, some enterprises have already entered mass production.
Due to structural constraints, judging from the current industry trends, the outer rotor hub motor is most likely to make a breakthrough in the electric bus, while the wheel motor solution may be more suitable in the field of heavy-duty trucks. In addition, the outer rotor hub motor may be the first to make breakthroughs in some special fields such as military off-road and mining electric wheels.
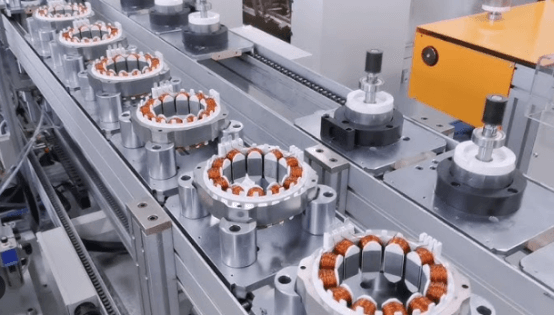
HONEST Automation has successfully developed hub motor automation assembly equipment and can provide customized automation solutions according to customer needs.
Related News